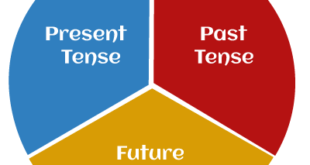
Tenses There are three basic tenses in the English language. Present Tense Past Tense Future Tense Every basic tense has four sub-tenses. Simple or Indefinite Tense Continuous or Progressive Tense Perfect Tense Perfect Continuous Tense Present Tense Simple or present Indefinite Tense Continuous or Present Progressive Tense Perfect Tense Perfect Continuous Tense Past Tense Simple or Past Indefinite Tense Continuous or …
Read More »Tag Archives: grammar
Verb: Learning English Grammar
Verb There are three (3) forms of the verb. Do Form Be Form Have Form Elaboration Do form refers to do, does, did. Be form refers to is, am, are, was, were, been, being. Have form refers to have, has, had. Main Verbs There are five (5) types of main verbs. Base Form Base Form (with s/es) Present Participle Simple …
Read More » FFK Blog Travel With Me
FFK Blog Travel With Me